Webhooks
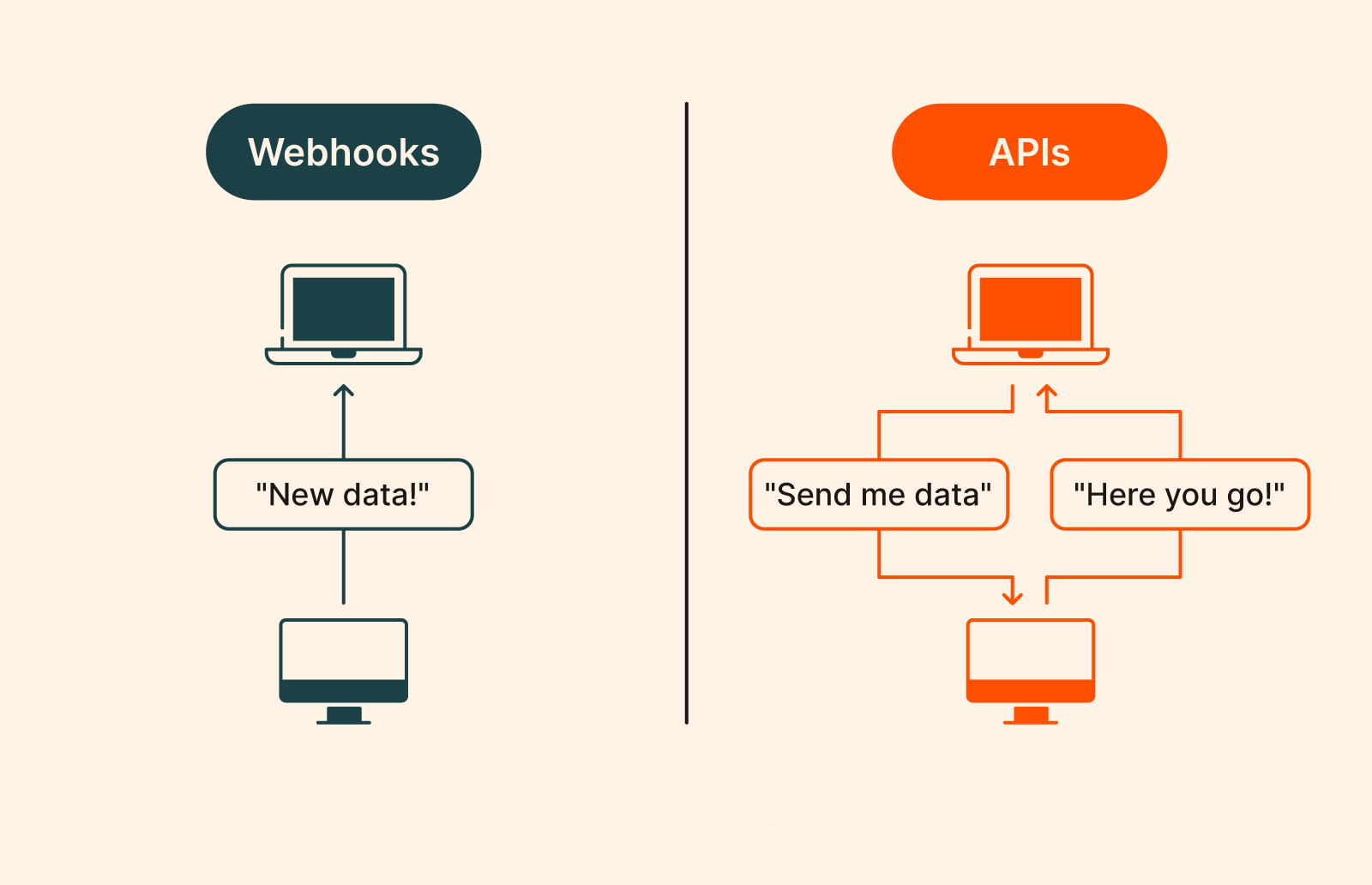
Webhooks enable your application to receive real-time notifications when important events occur in TurboSign. Instead of polling for changes, webhooks push event data to your specified endpoints immediately when signature documents are completed or voided.
Overview
TurboSign webhooks provide a robust and secure way to integrate document signature events into your existing workflows. When configured, webhooks will automatically send HTTP POST requests to your specified URLs whenever subscribed events occur.
Key Features
- Real-time Notifications: Receive instant updates when documents are signed or voided
- Multiple URLs: Configure up to 5 webhook URLs per configuration
- Secure Authentication: HMAC-SHA256 signature verification ensures webhook authenticity
- Reliable Delivery: Automatic retry logic with up to 3 attempts per webhook
- Delivery History: Track and replay webhook deliveries with detailed logs
- Event Filtering: Subscribe only to the events you need
Configuration
Setting Up Webhooks
Webhooks can be configured through the TurboSign interface in your organization settings.
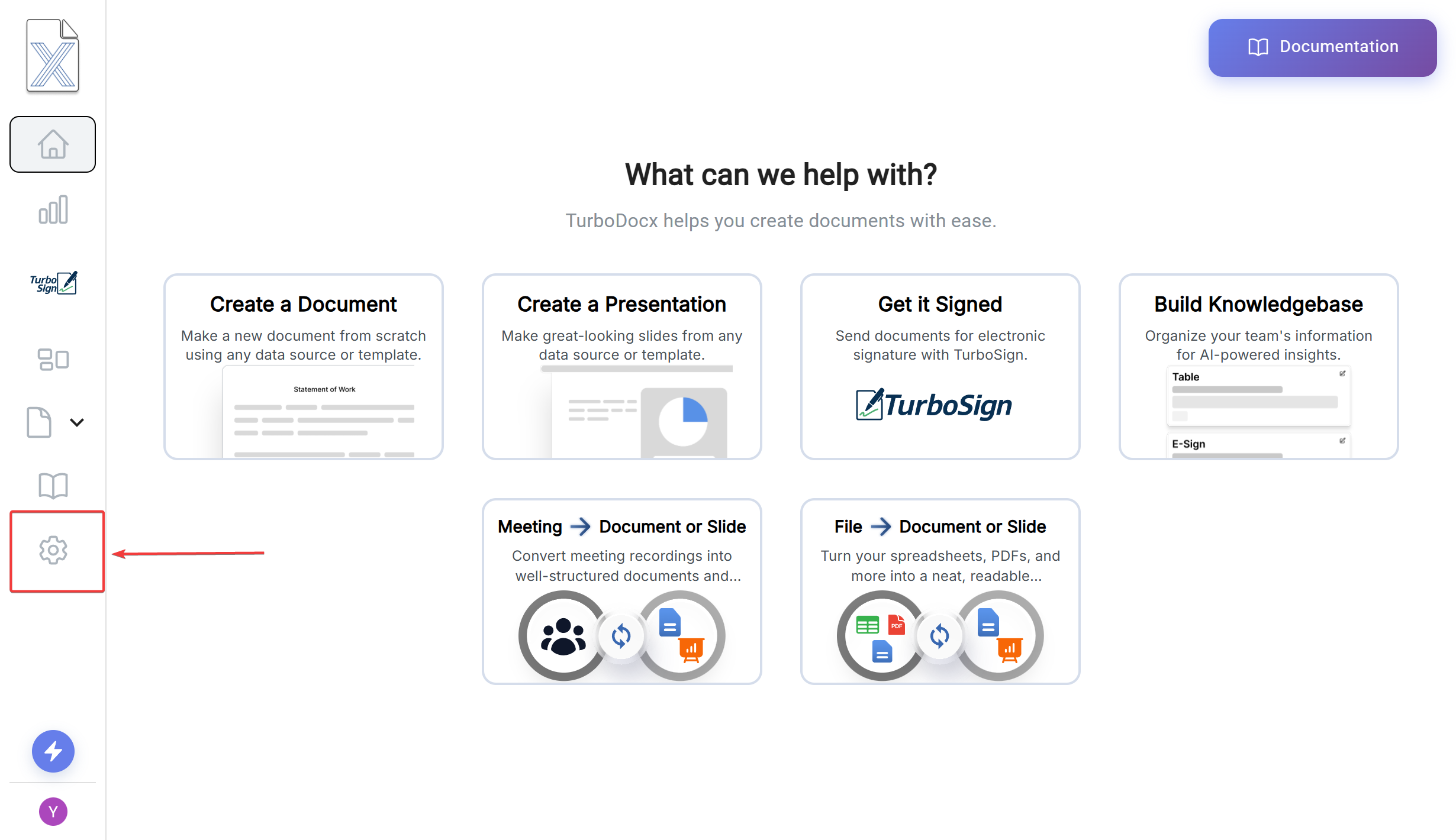
- Go to the Turbodocx Home Page and click on settings
- click on the settings on the sidemenu
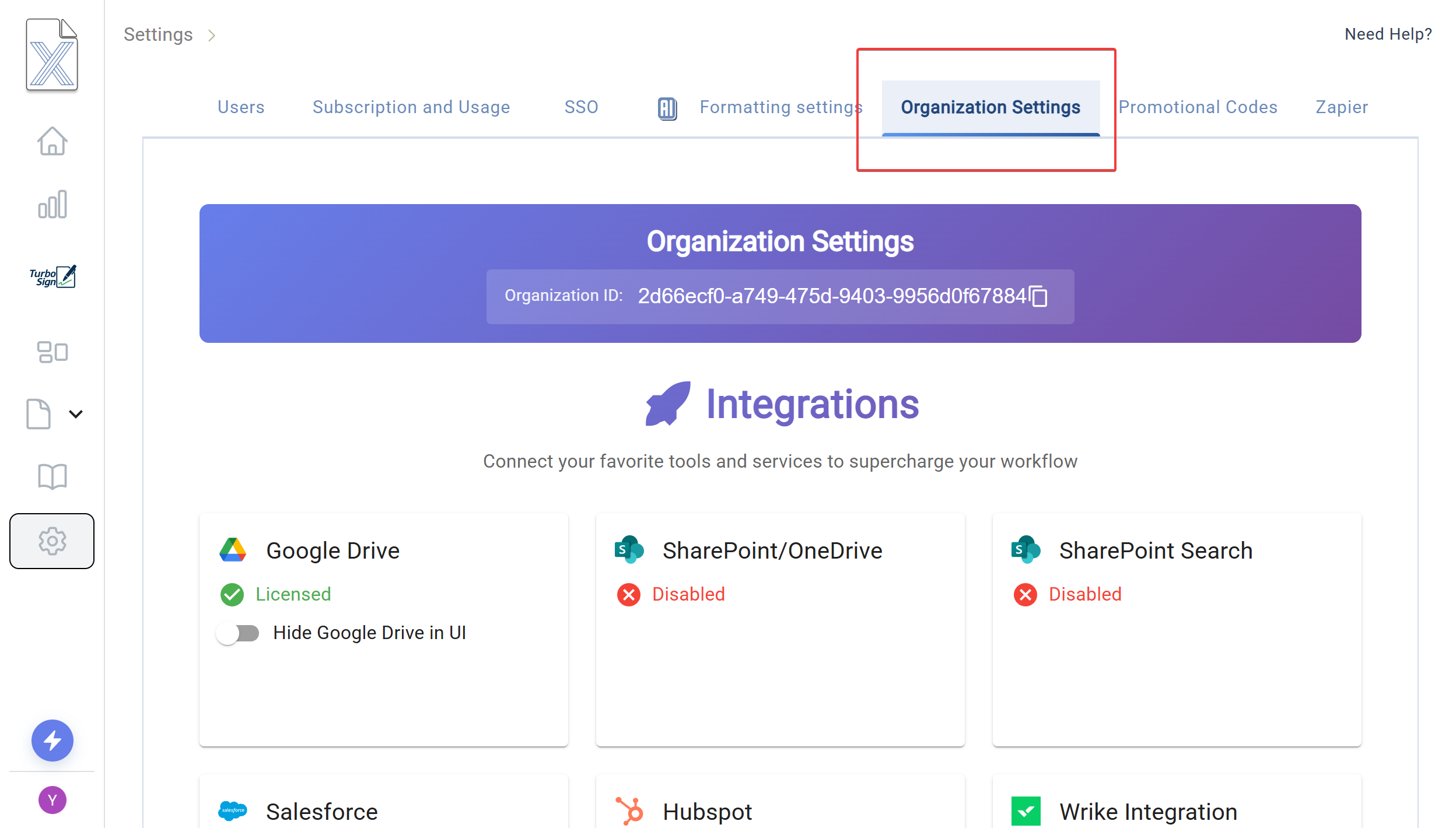
- Navigate to Organization Settings
- Select "Organization Settings" from the tabs
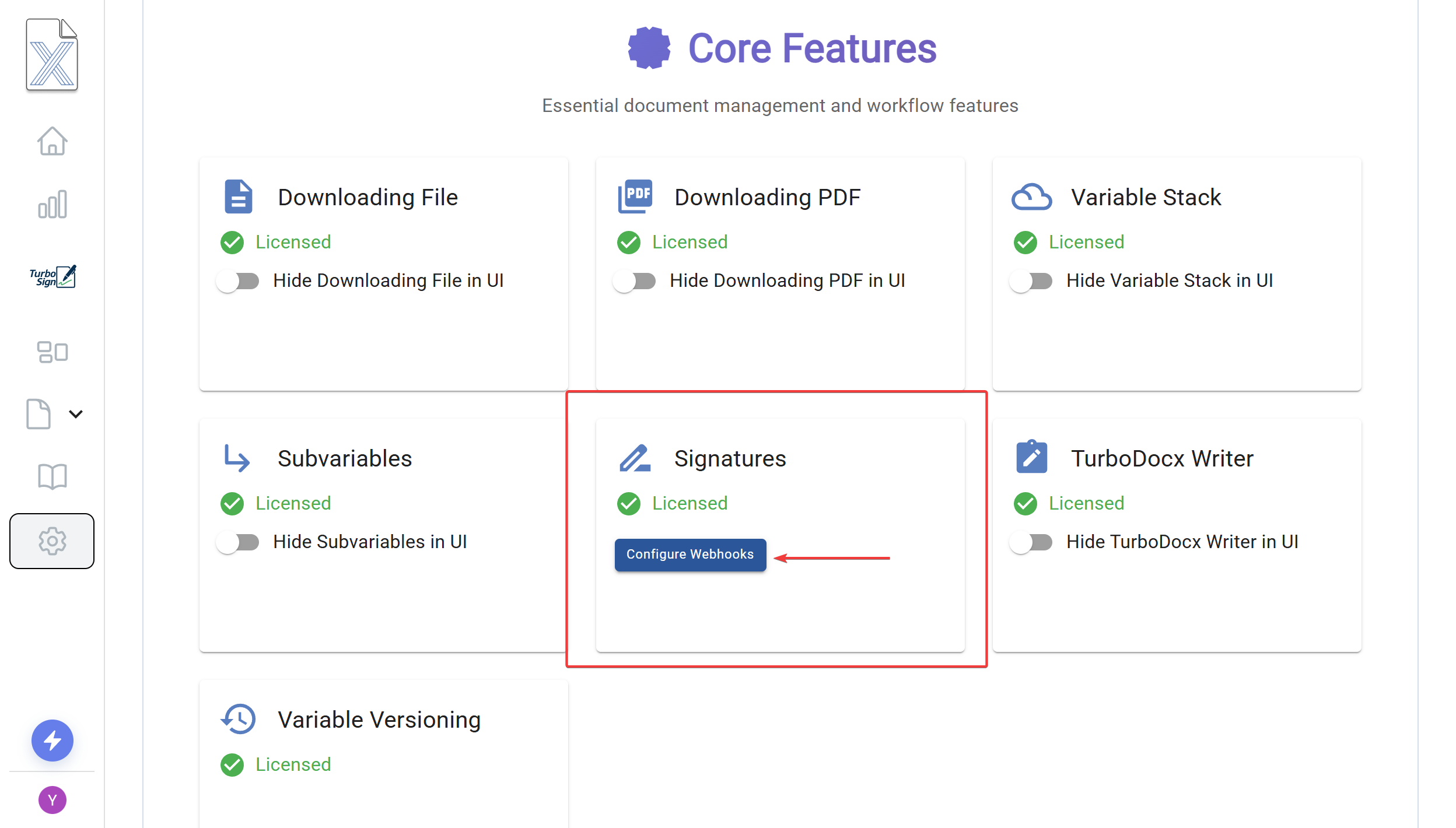
Scroll Down to Signature Configuration
- click "Configure Webhooks"
- Add Webhook URLs
- Enter your webhook endpoint URL(s)
- You can add up to 5 different URLs
- Each URL will receive all subscribed events
- URLs must use HTTPS for production environments
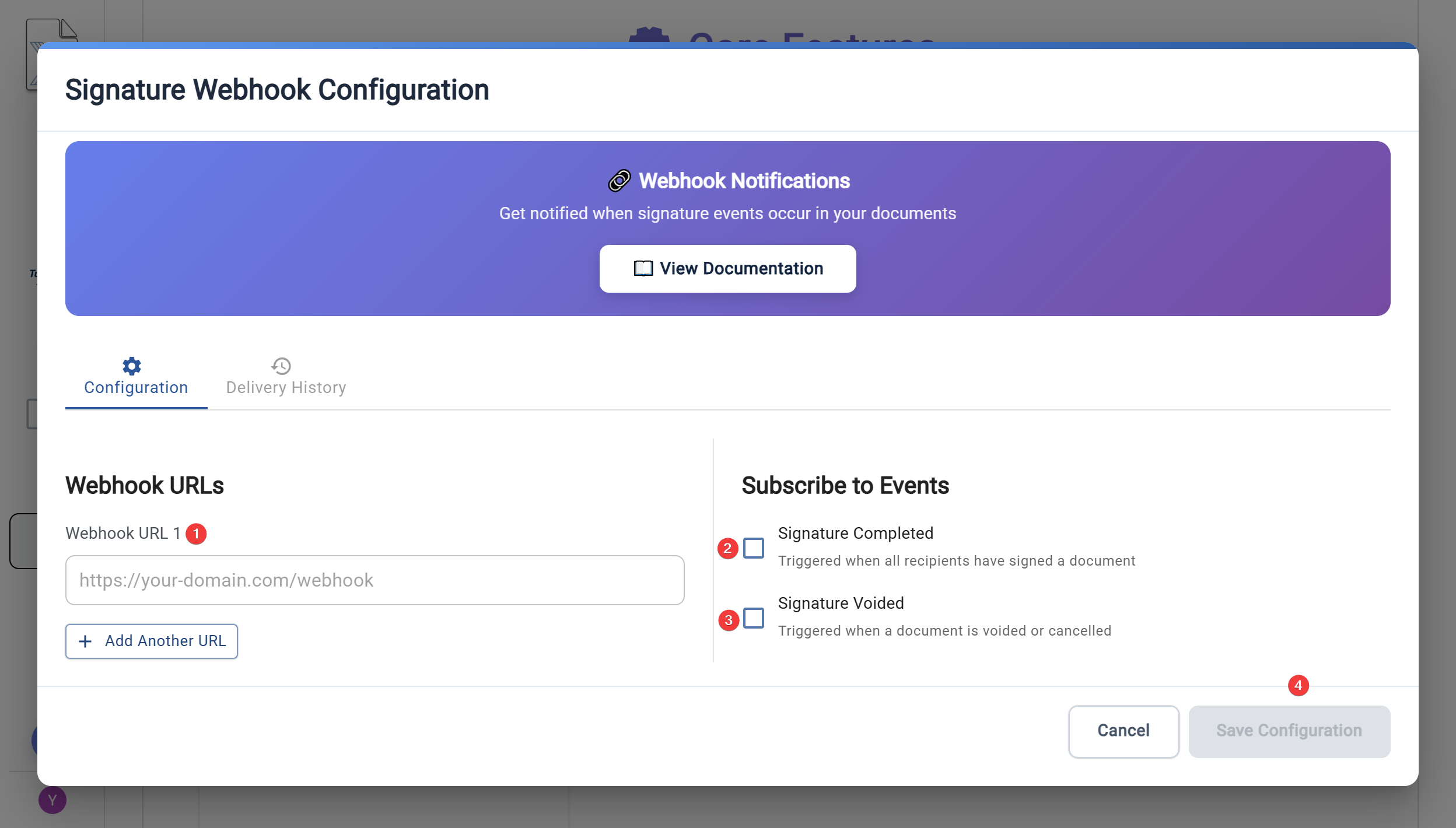
- Select Events to Subscribe
- Choose which events should trigger webhooks:
- Signature Document Completed: Triggered when all signers have completed signing
- Signature Document Voided: Triggered when a document is voided/cancelled
- Choose which events should trigger webhooks:

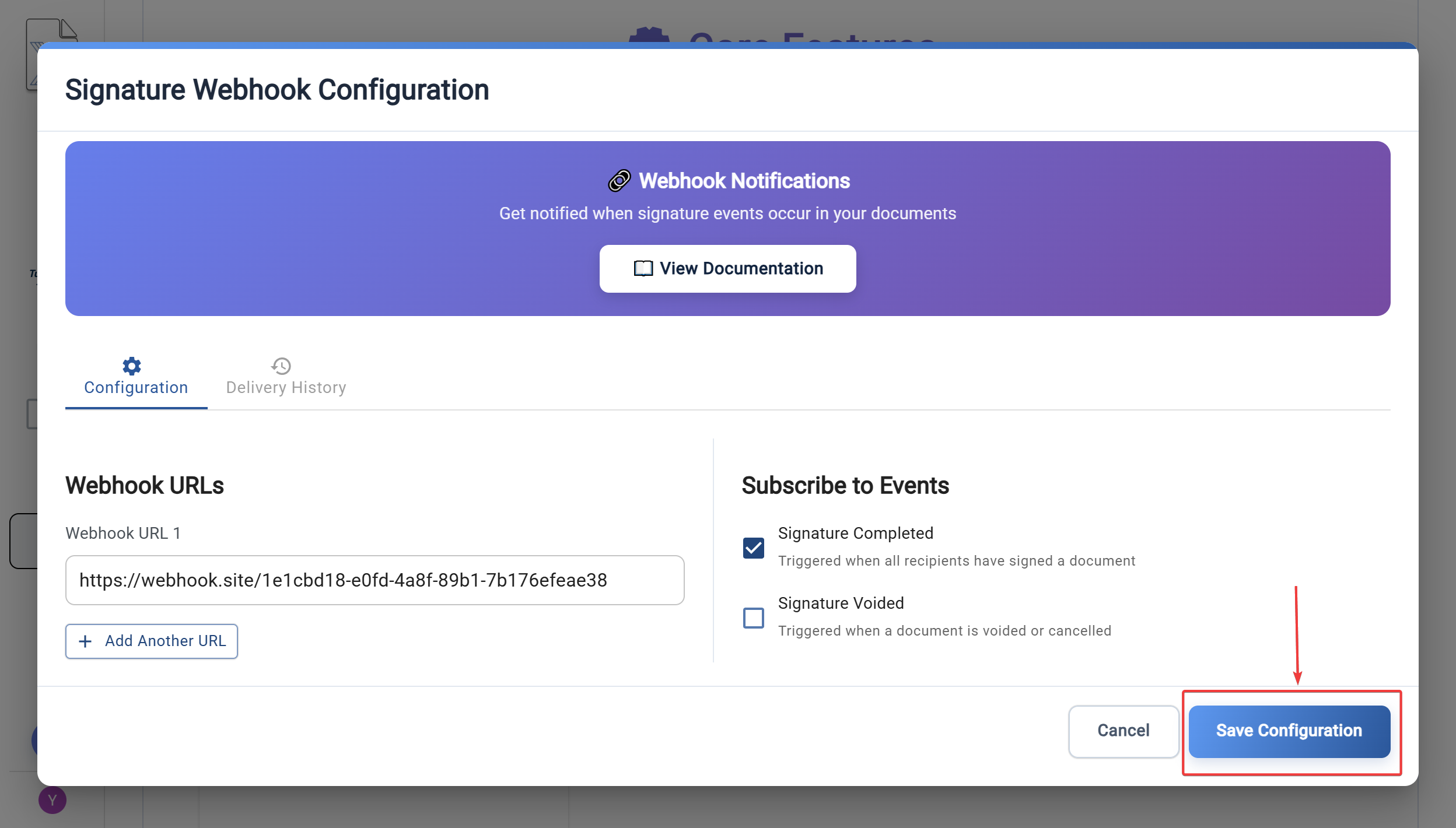
- Save Configuration
- Click "Save Configuration" to activate your webhooks
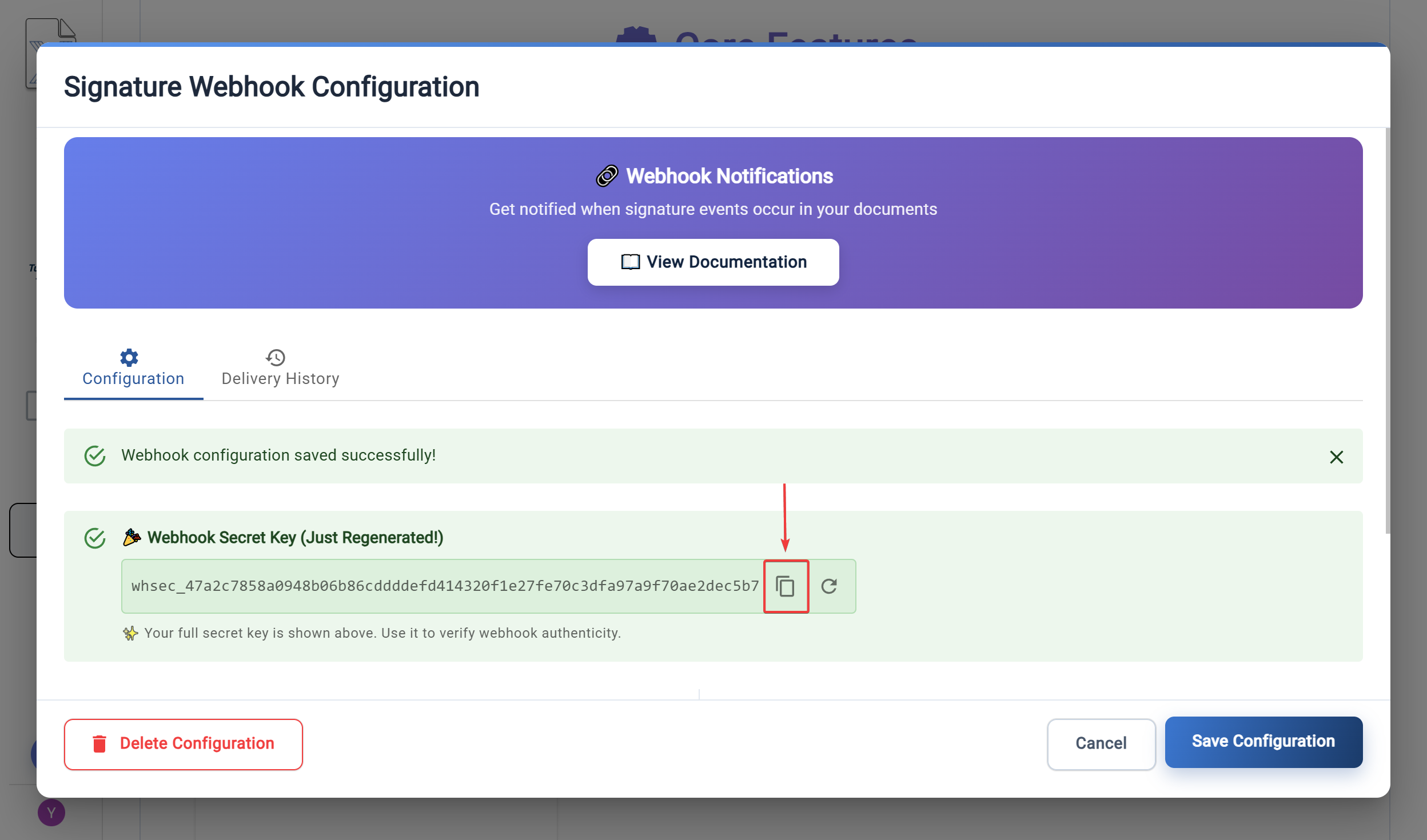
- Your webhook secret key will be displayed (only shown once for new configurations)
- Important: Copy and securely store your webhook secret - it won't be shown again
Managing Webhook Configuration
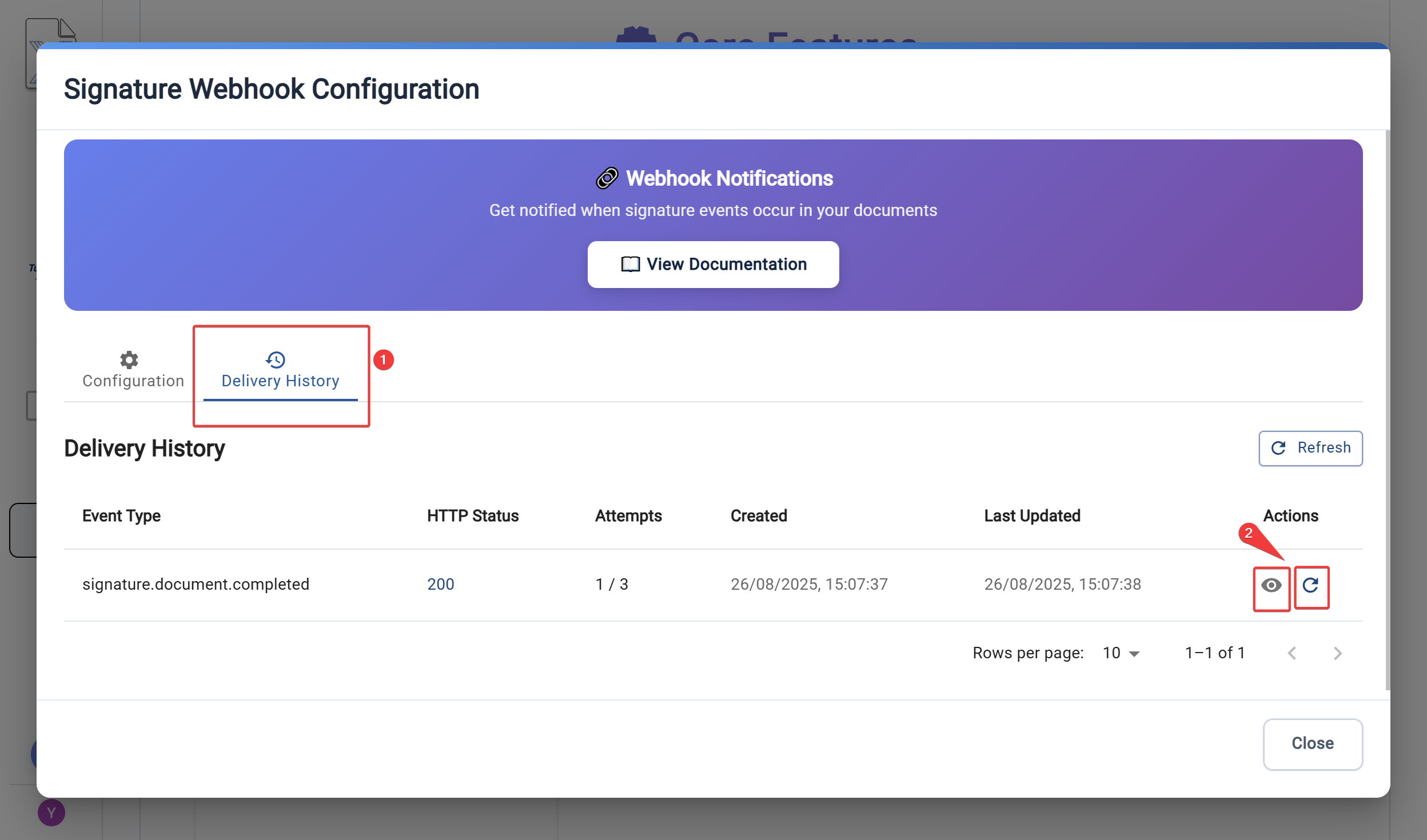
Viewing Delivery History
The Delivery History tab shows all webhook delivery attempts with detailed information:
- Event Type: The type of event that triggered the webhook
- HTTP Status: Response status code from your endpoint
- Attempts: Number of delivery attempts made
- Timestamps: When the webhook was created and last updated
- Actions: View details or replay failed deliveries
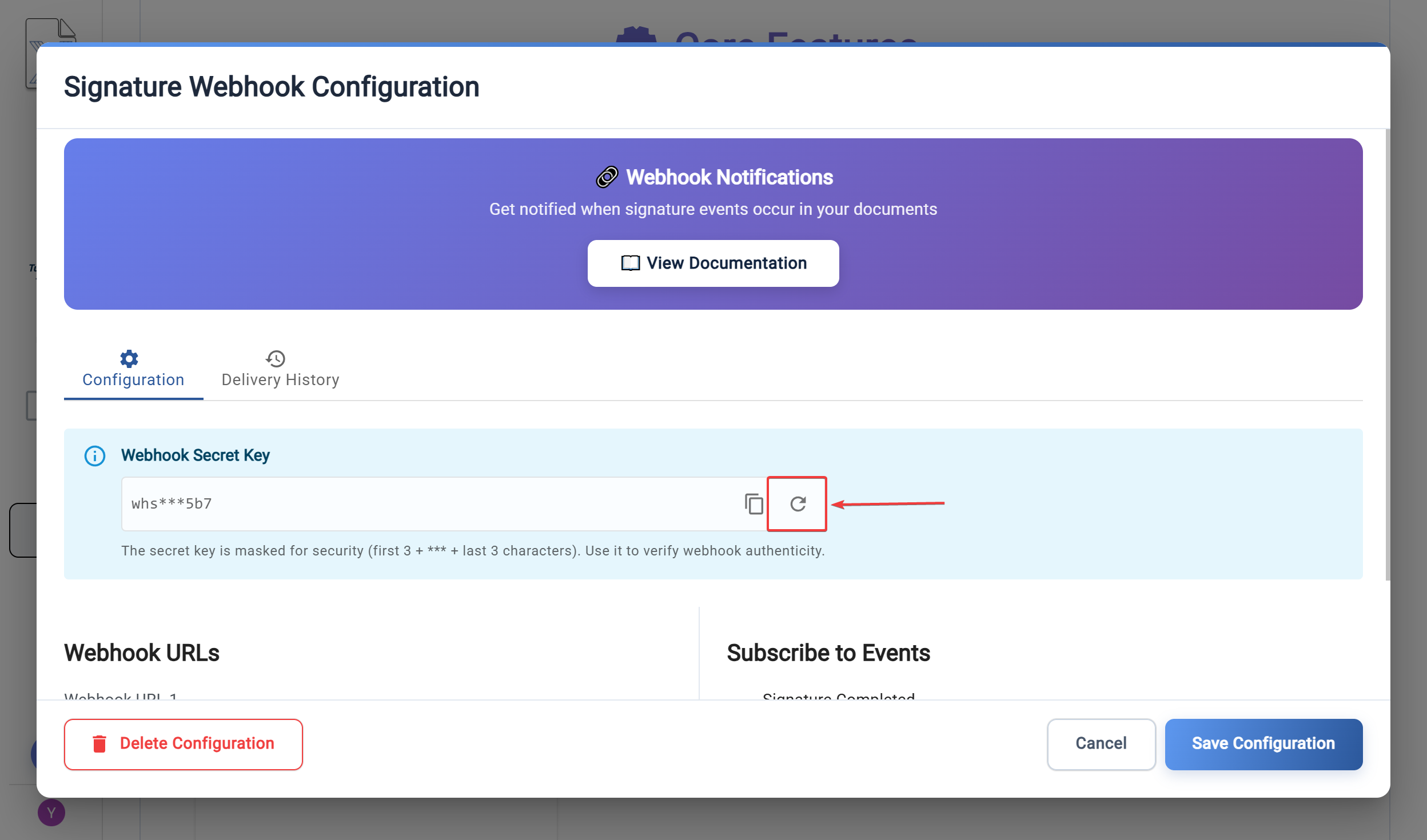
Webhook Secret Management
Your webhook secret is used to verify that webhooks are genuinely from TurboDocx:
- Initial Generation: A secret is automatically generated when you create a webhook configuration
- Security: The secret is only shown in full immediately after generation or regeneration
- Regeneration: You can regenerate the secret at any time if compromised
- Display: After initial viewing, only a masked version (first 3 + *** + last 3 characters) is shown
Webhook Events
Signature Document Completed
Triggered when all required signers have successfully signed a document.
Event Name: signature.document.completed
Payload Example:
{
"event": "signature.document.completed",
"event_id": "evt_01daa4ba531c42938f861c5a9ce9a5f2",
"created_at": "2025-08-26T11:44:30.305Z",
"version": "1.0",
"data": {
"document_id": "2dea093d-c38f-4898-b440-43dd9a14cd9d",
"title": "Document Name",
"status": "completed",
"status_enum": "SignatureDocumentStatus.COMPLETED",
"completed_at": "2025-08-26T11:44:30.299Z",
"document_hash": "f516c4b9de36a5c9a999ba87abbc93078fdd0c9f6b855590d883d8bfb143308f"
}
}
Signature Document Voided
Triggered when a document is voided or cancelled.
Event Name: signature.document.voided
Payload Example:
{
"event": "signature.document.voided",
"event_id": "evt_c825f202658b41ea932871ba13cc52a5",
"created_at": "2025-08-26T11:42:03.622Z",
"version": "1.0",
"data": {
"document_id": "9eee553b-28b6-4b43-b52b-4ef9957cc503",
"title": "Statement of Work Example Draft",
"status": "voided",
"status_enum": "SignatureDocumentStatus.VOIDED",
"voided_at": "2025-08-26T11:42:03.582Z",
"void_reason": "signature not required",
"document_hash": "b19151b93aed4f8cbcf060030a338dd414c249914eb8d2591c72390a0fa1b754"
}
}
Payload Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
event | string | The type of event (e.g., signature.document.completed) |
event_id | string | Unique identifier for this event instance |
created_at | string | ISO 8601 timestamp when the event occurred |
version | string | Webhook payload version (currently "1.0") |
data.document_id | string | Unique identifier of the signature document |
data.title | string | Document title/name |
data.status | string | Human-readable status |
data.status_enum | string | Programmatic status enum value |
data.document_hash | string | Document content hash for integrity verification |
data.completed_at | string | When the document was completed (completed event only) |
data.voided_at | string | When the document was voided (voided event only) |
data.void_reason | string | Reason for voiding (voided event only) |
Signature Verification
Every webhook request includes an x-turbodocx-signature header that you should verify to ensure the webhook is genuinely from TurboDocx.
How It Works
- TurboDocx creates a signature using HMAC-SHA256
- The signature is computed from:
timestamp + "." + request_body - The signature is sent in the
x-turbodocx-signatureheader - Your endpoint verifies this signature using your webhook secret
Verification Headers
Each webhook request includes these headers:
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
X-TurboDocx-Signature | HMAC signature for verification (format: sha256=<hex>) |
X-TurboDocx-Timestamp | Unix timestamp when the webhook was sent |
X-TurboDocx-Event | The event type that triggered this webhook |
X-TurboDocx-Delivery-Id | Unique ID for this delivery attempt (for idempotency) |
Try it Now
SDK Verification Examples
Our SDKs include built-in webhook verification. Here are examples for each language:
- JavaScript
- Python
- Go
- .NET
- Ruby
import { verifyWebhookSignature } from '@turbodocx/sdk';
import express from 'express';
const app = express();
app.post('/webhook', express.raw({ type: 'application/json' }), (req, res) => {
const isValid = verifyWebhookSignature({
signature: req.headers['x-turbodocx-signature'],
timestamp: req.headers['x-turbodocx-timestamp'],
body: req.body,
secret: process.env.TURBODOCX_WEBHOOK_SECRET
});
if (!isValid) {
return res.status(401).json({ error: 'Invalid signature' });
}
const event = JSON.parse(req.body.toString());
// Process event...
res.status(200).json({ received: true });
});
from turbodocx import verify_webhook_signature
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, HTTPException
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/webhook")
async def handle_webhook(request: Request):
body = await request.body()
is_valid = verify_webhook_signature(
signature=request.headers.get("x-turbodocx-signature"),
timestamp=request.headers.get("x-turbodocx-timestamp"),
body=body,
secret=os.environ["TURBODOCX_WEBHOOK_SECRET"]
)
if not is_valid:
raise HTTPException(status_code=401, detail="Invalid signature")
event = json.loads(body)
# Process event...
return {"received": True}
func webhookHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
body, _ := io.ReadAll(r.Body)
isValid := sdk.VerifyWebhookSignature(
r.Header.Get("X-TurboDocx-Signature"),
r.Header.Get("X-TurboDocx-Timestamp"),
body,
os.Getenv("TURBODOCX_WEBHOOK_SECRET"),
)
if !isValid {
http.Error(w, "Invalid signature", http.StatusUnauthorized)
return
}
var event sdk.WebhookEvent
json.Unmarshal(body, &event)
// Process event...
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> HandleWebhook()
{
using var reader = new StreamReader(Request.Body);
var body = await reader.ReadToEndAsync();
var isValid = WebhookVerifier.VerifySignature(
Request.Headers["X-TurboDocx-Signature"],
Request.Headers["X-TurboDocx-Timestamp"],
body,
_configuration["TurboDocx:WebhookSecret"]
);
if (!isValid)
return Unauthorized("Invalid signature");
var webhookEvent = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<WebhookEvent>(body);
// Process event...
return Ok(new { Received = true });
}
def turbodocx_webhook
body = request.raw_post
is_valid = TurboDocx::WebhookVerifier.verify(
signature: request.headers['X-TurboDocx-Signature'],
timestamp: request.headers['X-TurboDocx-Timestamp'],
body: body,
secret: ENV['TURBODOCX_WEBHOOK_SECRET']
)
unless is_valid
return render json: { error: 'Invalid signature' }, status: :unauthorized
end
event = JSON.parse(body)
# Process event...
render json: { received: true }
end
Security Best Practices
- Always verify signatures: Never process webhooks without verifying the signature
- Use HTTPS: Always use HTTPS endpoints in production
- Store secrets securely: Keep webhook secrets in environment variables or secure vaults
- Implement timestamp validation: Reject webhooks with timestamps older than 5 minutes
- Use timing-safe comparison: Prevent timing attacks when comparing signatures
- Handle retries idempotently: Use the
X-TurboDocx-Delivery-Idto prevent duplicate processing - Respond quickly: Return 200 OK immediately and process webhooks asynchronously
- Log failures: Keep logs of signature verification failures for security monitoring
Delivery & Retries
Delivery Behavior
- Timeout: Each delivery attempt has a 10-second timeout
- Success Criteria: Only HTTP 2xx status codes are considered successful
- Retry Logic: Failed deliveries are automatically retried up to 3 times
- Retry Schedule: Exponential backoff between retry attempts
- Delivery Order: Webhooks are delivered to all configured URLs in parallel
Handling Failures
When a webhook delivery fails:
- Automatic Retries: The system will automatically retry failed deliveries
- Delivery History: All attempts are logged in the delivery history
- Manual Replay: You can manually replay failed deliveries from the UI
- Error Details: Response status codes and error messages are captured
Best Practices for Your Endpoint
- Return 200 OK quickly: Process webhooks asynchronously to avoid timeouts
- Implement idempotency: Handle duplicate deliveries gracefully
- Queue for processing: Use a message queue for reliable processing
- Monitor your endpoint: Set up alerting for webhook processing failures
- Handle all event types: Be prepared for new event types in the future
Testing Webhooks
Using the Test Feature
You can test your webhook configuration before going live:
- Configure your webhook with your test endpoint URL
- Save the configuration to activate it
- Create a test signature document and complete the signing process
- Check the Delivery History to verify successful delivery
- Verify your endpoint received and processed the webhook correctly
Development Tools
For local development, consider using:
- ngrok: Expose your local server to receive webhooks
- Webhook.site: Test webhook payloads without writing code
- RequestBin: Inspect webhook requests in real-time
- Postman: Simulate webhook requests for testing
Testing Checklist
- Webhook endpoint returns 200 OK status
- Signature verification is working correctly
- Timestamp validation is implemented
- All event types are handled
- Error handling is in place
- Retry logic is handled idempotently
- Logs capture webhook processing details
- Performance under load has been tested
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Webhook Not Receiving Events
Symptoms: Events occur but webhooks aren't triggered
Solutions:
- Verify webhook configuration is saved and active
- Check that you've subscribed to the correct events
- Ensure your endpoint URL is correct and accessible
- Review the Delivery History for error messages
Signature Verification Failing
Symptoms: 401 Unauthorized responses from your endpoint
Solutions:
- Ensure you're using the raw request body (not parsed JSON)
- Verify the webhook secret matches exactly
- Check that header names are lowercase in your code
- Confirm timestamp validation isn't too strict
Timeouts
Symptoms: Webhook deliveries show timeout errors
Solutions:
- Return 200 OK immediately, process asynchronously
- Optimize endpoint performance
- Check network connectivity and firewall rules
- Consider increasing server resources
Duplicate Deliveries
Symptoms: Same event processed multiple times
Solutions:
- Implement idempotency using
X-TurboDocx-Delivery-Id - Store processed event IDs temporarily
- Use database constraints to prevent duplicates
Getting Help
If you encounter issues not covered here:
- Check the Delivery History for detailed error messages
- Review your endpoint logs for processing errors
- Test with a simple endpoint to isolate issues
- Contact Support with your webhook configuration details and error messages
API Reference
Webhook Object
{
"id": "webhook_abc123",
"orgId": "org_xyz789",
"name": "signature",
"urls": [
"https://api.example.com/webhooks/turbosign",
"https://backup.example.com/webhooks"
],
"events": ["signature.document.completed", "signature.document.voided"],
"secretExists": true,
"maskedSecret": "whs***f6a",
"isActive": true,
"createdOn": "2024-01-15T09:00:00.000Z",
"updatedOn": "2024-01-15T09:00:00.000Z"
}
Delivery Object
{
"id": "delivery_def456",
"webhookId": "webhook_abc123",
"eventType": "signature.document.completed",
"url": "https://api.example.com/webhooks/turbosign",
"httpStatus": 200,
"attemptCount": 1,
"maxAttempts": 3,
"isDelivered": true,
"deliveredAt": "2024-01-15T10:30:05.000Z",
"createdOn": "2024-01-15T10:30:00.000Z",
"updatedOn": "2024-01-15T10:30:05.000Z"
}